Strengthening Prevention in Integrated Care Systems (The Framework) is Queensland’s framework for reducing preventable chronic disease. It focuses on chronic diseases that can be prevented by addressing modifiable risk factors such as poor nutrition, physical inactivity, smoking/vaping and harmful alcohol use.*
The Framework is designed to build Integrated Care Systems that collectively drive the shift to a stronger, more connected approach to chronic disease prevention. Guiding principles and building blocks provide the ‘key ingredients’ for partners across health, community and social care sectors to strengthen prevention together.*
*The Framework is aligned to Health and Wellbeing Queensland’s remit; however, it could be applied beyond the identified scope.
What are Integrated Care Systems?
Integrated Care Systems (ICS) bring together committed leaders from organisations that shape the health and wellbeing of communities. While their composition varies by region, ICSs may include:
- Health services
- Community organisations
- All levels of government
- Social enterprises
- Not-for-profit organisations
- Private sector and industry
- Researchers and academics
With shared cross-sector commitment, ICSs set the strategic direction for local approaches that strengthen chronic disease prevention. They turn commitment into action by involving relevant partners across agencies, the workforce and the community. The Framework’s building blocks provide the right foundations to reshape preventive health to meet the unique needs and priorities of the region.
Health and Wellbeing Queensland developed The Framework to enable meaningful collaboration and provide the foundations for a coordinated, cross-sector approach to sustainable chronic disease prevention.
We have a real opportunity to unite for maximum collective impact – working together to deliver preventive health differently and to strengthen, scale and spread innovation already happening across Queensland. Rather than silos and duplication of effort, a shared vision across agencies enables skills, expertise and resources to be leveraged and mobilised for a sustainable prevention ecosystem that:
Leaders from organisations that influence the health and wellbeing of communities are encouraged to establish ICSs that drive system wide change toward proactive prevention. This requires collaboration with multi-agency partners, workforce and communities themselves. Advancing the prevention agenda calls for leadership with the capacity to move beyond daily system pressures and champion transformative, sustainable change.
Together we can strengthen chronic disease prevention at the people and community, service, and system levels.
About prevention
Why does chronic disease prevention matter?
We must do more to prevent chronic disease, not just treat it. By reducing preventable illness, we can support better health outcomes for Queenslanders and a more sustainable health system into the future.
of Queenslanders had at least one chronic disease (2022).
of Queensland's health burden could be prevented by addressing modifiable risk factors (2024).
spent on coronary heart disease (2022-23).
spent on type 2 diabetes (2022-23).
of deaths in Queensland were premature, and almost half could have been avoided with better healthcare or public health strategies (2022).
Preventable chronic diseases are long term conditions with modifiable risk factors. Chronic disease prevention spans the prevention spectrum – wider determinants of health, primary, secondary, and tertiary prevention.
- Wider determinants of health: Social, cultural, economic and environmental factors that influence an individual’s health outcomes are foundational to delivery of prevention – improving health and wellbeing for all.
- Primary prevention: Universal access to health information, tools and programs that support positive health behaviours, preventing the onset of chronic disease – keeping people well in the community, and out of hospital.
- Secondary prevention: Targeted approaches that reach those at increased risk of developing chronic disease for timely identification and early intervention – lowering future healthcare demand.
- Tertiary prevention: Proactive, personalised care for those already living with chronic disease to slow progression and maintain quality of life – reducing complications and healthcare utilisation.
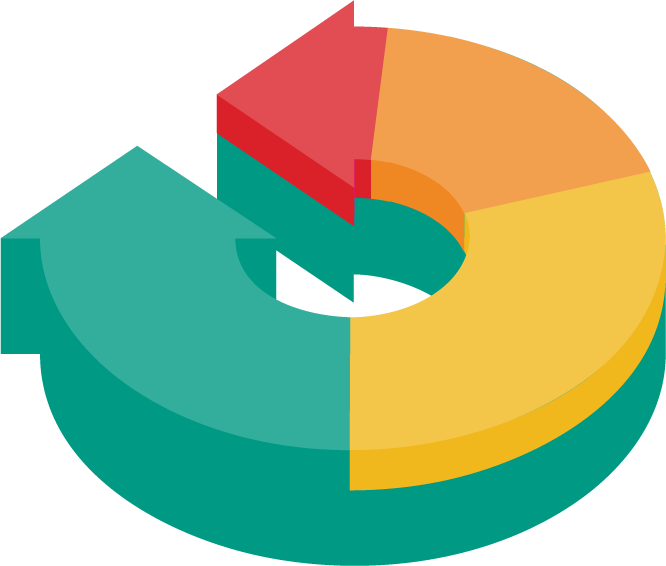
Spectrum of prevention

-
Tertiary prevention:
Reducing complications and healthcare utilisation
-
Secondary prevention:
Lowering future healthcare demand
-
Primary prevention:
Keeping people well and out of hospital
-
Wider determinants of health:
Improving health and wellbeing for all
Addressing the wider determinants of health and investing in primary prevention will have a transformative impact on reducing chronic disease in the long term. At the same time, targeted interventions and personalised care in secondary and tertiary prevention will help ease health care demand and utilisation in the short term.
Last updated 26 May 2025